Potato diseases cause significant losses to any farm and can lead to crop degeneration. The main types of diseases: fungal, bacterial, viral. Common causes are contaminated planting material, soil, and the remains of infected plants in the ground. Various disease control methods are used to protect the crop.
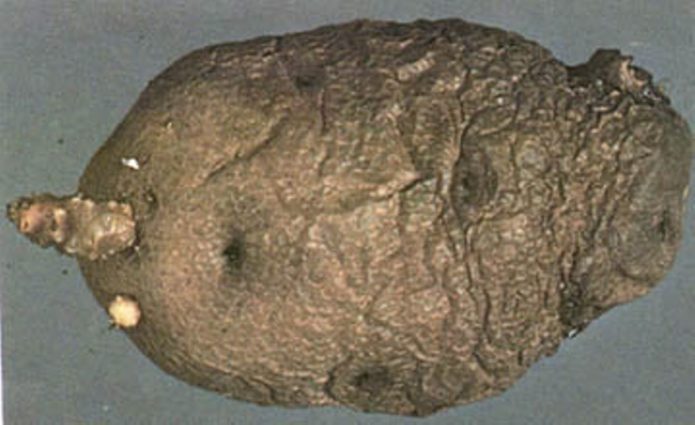
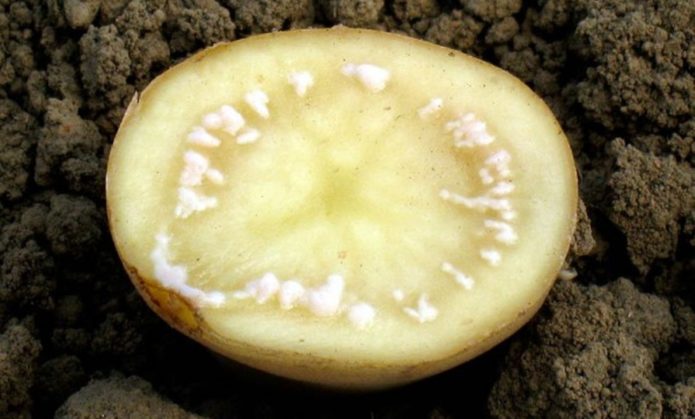
Fusarium wilting and dry rot of tubers
The causative agent of the disease is the Fusarium mushroom.
Common causes of fusarium wilt and rot:
- high humidity;
- high temperature.
Dry fusarium rot of potatoes develops during storage.
Reasons for infection:
- contaminated soil;
- an infection on the ground stuck to potatoes;
- the presence of mechanical damage;
- damage by pests;
- during storage of the crop, the fungus from infected potatoes spreads to nearby tubers;
- not disinfected storage areas.
Fighting the disease:
- treatment of potatoes with Borogum, Fitosporin before planting and Fitosporin storage before laying for the winter;
- disinfection of soil with potassium permanganate, preparations of 33 Bogatyr, Boss-Batiushka;
- disinfection of storage facilities.
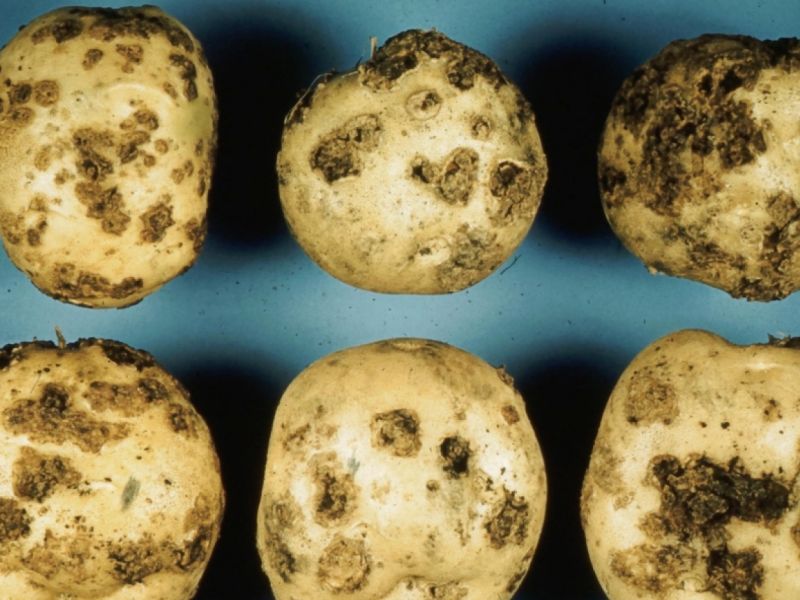
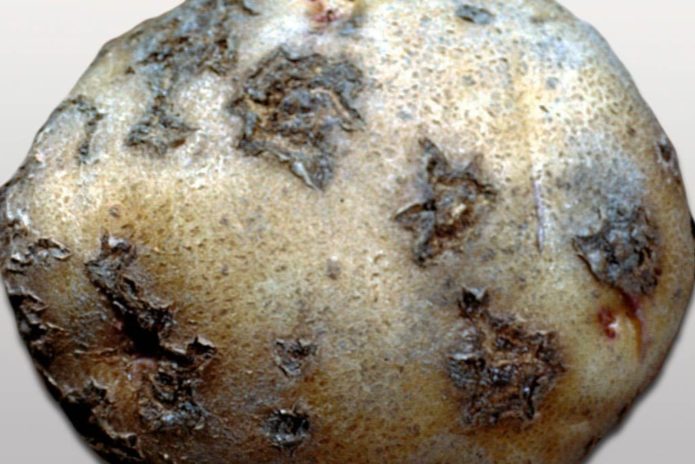
Black scab (rhizoctonia)
The causative agent is rhizoctonia, another name is basidiomycete.
The main factors of infection:
- early planting dates;
- landing at great depth;
- excessive soil moisture;
- temperature above + 18 ° C;
- non-compliance with crop rotation;
- the presence of fungal mycelium in the ground, on weeds, plant residues (undecomposed mechanical inclusions of plants);
- late harvesting of culture.
Wrestling:
- antifungal preparation of seed tubers with drugs effective against rhizoctonia, for example: Fitosporin, Baktofit, Fenoram, Planriz, Integral, Maxim, Utan;
- disinfection of soil;
- crop rotation (the best predecessors of potatoes are cereals);
- culling of affected seed potatoes;
- planting at soil temperatures above 8 ° C;
- cleaning in dry weather.
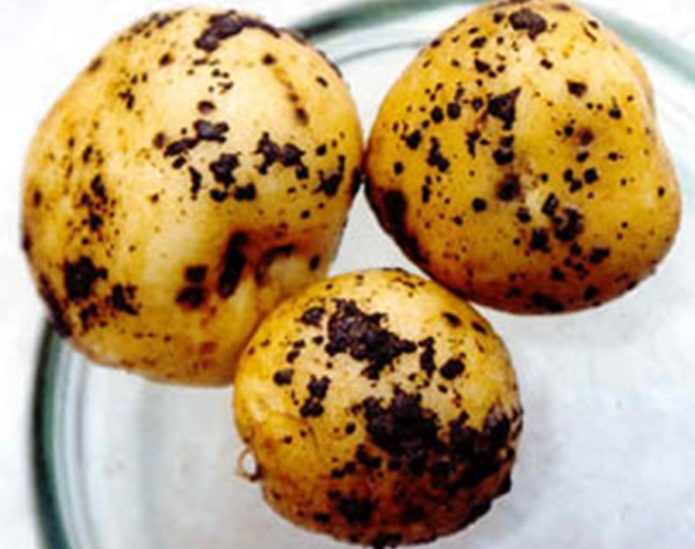
Common scab
Source of infection - radiant fungus.
Causes:
- Hot Summer;
- temperature over 25 ° C;
- liming the land in the year of cultivation;
- pH more than 5.5;
- introduction of fresh manure;
- the presence of mechanical damage on potatoes;
- excess nitrogen fertilizers;
- lack of boron and manganese in the soil;
- infected plant remains.
Protective measures:
- preliminary sowing of green manure crops (lupine, vetch, mustard);
- the use of acidic fertilizers (superphosphate, ammonium sulfate, potassium magnesium);
- introduction of trace elements (copper, boron, manganese);
- dressing of tubers (nitrafen 35%, polycarbacin 75%, TMTD 80%);
- soil disinfection;
- using healthy seed.
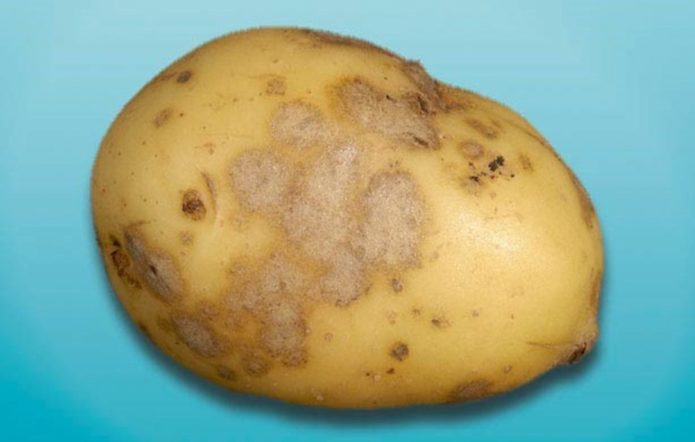
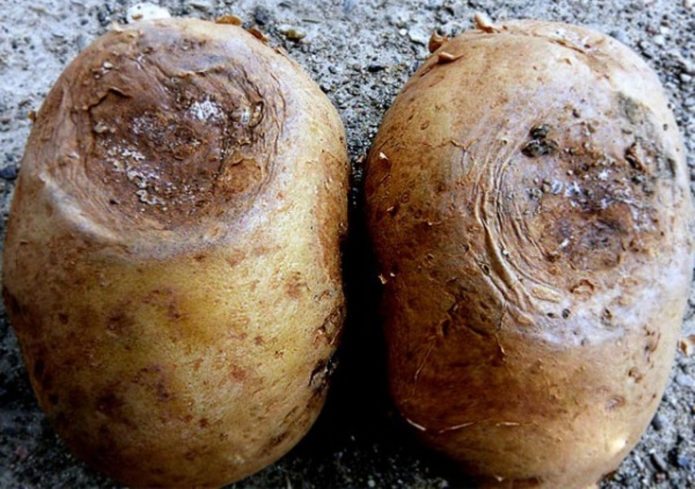
Silvery scab
The carrier of the disease is the fungus Spondylocladium atrovirens.
Sources of the disease:
- affected planting material;
- contaminated soil;
- storage temperature over 3 ° C;
- high humidity.
Ways to fight:
- processing of potatoes immediately after harvesting with Titusim, Vivatax 200, Botran, Tekto 450, Celest, Nitrafen, Fundazol and potassium permanganate earth;
- maintaining the optimal temperature in the storage;
- ventilation to reduce humidity.
Fomoz of potatoes
Causative agents: fungi of the genus Phoma exiqua.
Reasons for infection:
- infected tubers;
- the remains of infected plants in the ground;
- rain and wind;
- impure storehouse.
Ways to fight:
- processing of potatoes before planting (Fitosporin, Borogum) and storage (Fitosporin storage);
- improvement of the soil with green manure, means of PuhoVita, Boss-father, 33 Bogatyr;
- compliance with the rules of crop rotation;
- mowing tops 2 weeks before harvesting;
- disinfection of storage.
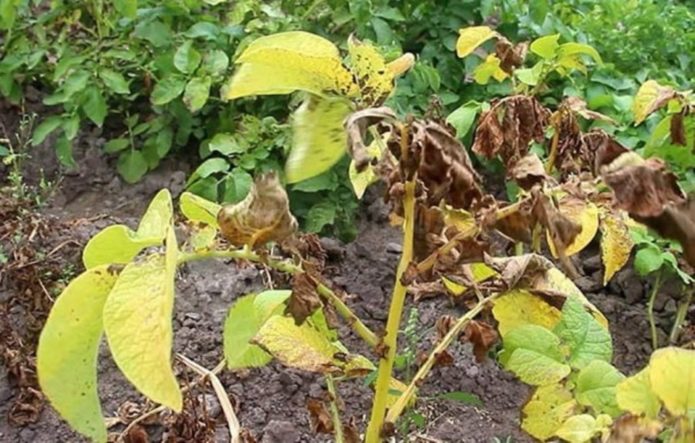
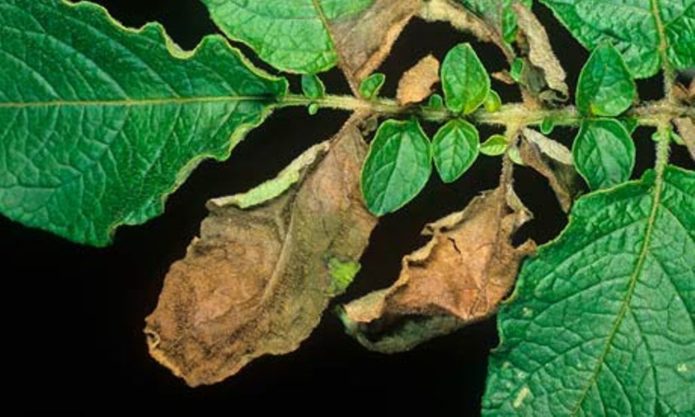
Late blight
The causative agent is the fungus Phytophthora infestans de Bary.
Causes:
- contaminated land;
- infected planting material;
- wet weather;
- wind;
- closing of tops in rows.
Protection and treatment:
- soil disinfection;
- treatment of tubers before storage with Fitosporin; storage;
- chemical spraying of plants with 1% Bordeaux liquid, oxychom, cuprokat;
- top dressing with potash fertilizers, microelements (copper, boron, manganese);
- alternation of cultures;
- planting early;
- harvesting in dry weather.
Dry Spot (Alternaria)
The spots on potatoes are caused by Alternaria fungi.
Causes:
- change from dry, hot weather to wet and vice versa;
- lack of nitrogen and potassium in the soil;
- wound damage to potatoes;
- excess phosphorus;
- little moisture;
- infected seed tubers.
Ways to fight:
- destruction of the primary infection;
- mineral fertilizing of crops;
- chemical treatments with fungicides, for example - Bordeaux liquid, sulfur, Revus Top, Bravo preparations;
- harvesting a fully ripe crop.
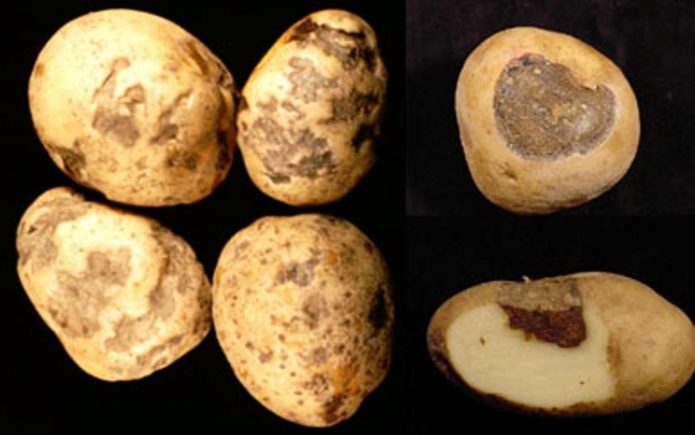
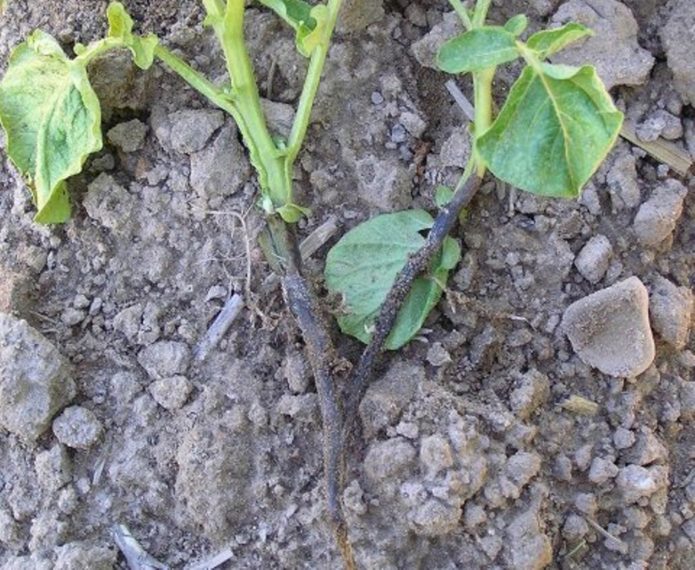
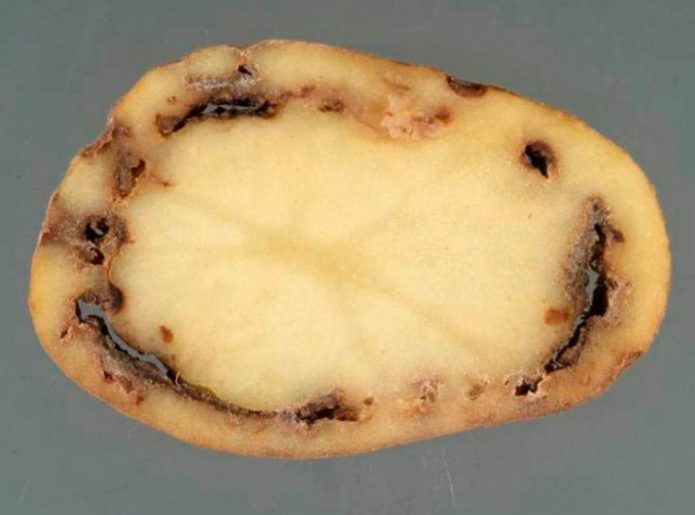
Ring rot
Bacterial lesions are caused by the pathogen Clavibacter michiganensis var. sepeilonicus.
Causes:
- the presence of infected plant debris;
- damaged tubers;
- the penetration of bacteria into the vascular system of new potatoes;
- infection of potatoes during harvest (damage from implements).
How to fight:
- destruction of infected plants;
- sterilizing the knife before cutting seed potatoes;
- compliance with crop rotation;
- antibacterial treatment of tubers;
- disinfection of soil with potassium permanganate;
- the use of healthy planting material.
Brown bacterial rot
The carrier of bacteria is Pseudomonas solanacearum.
Infection factors:
- contaminated soil;
- tubers;
- overwintered infected plant remains;
- weeds of the genus nightshade;
- nematodes and various insects;
- high soil moisture.
Protective measures:
- taking into account the rules of crop rotation (the best predecessors: beets, perennial grasses, wheat, legumes);
- weed control;
- disinfection of tubers (TMTD, Borogum, Fitosporin) and soil with potassium permanganate;
- drying potatoes after harvesting;
- avoidance of injury to potatoes during transportation and storage.
Blackleg
The causative agent is Pectobacterium.
Causes:
- the remains of infected plants in the ground; - here everything is good.
- the spread of bacteria by insect larvae;
- diseased tubers.
Wrestling:
- antibacterial treatment of soil and potatoes;
- weed control;
- harvesting tops before harvesting;
- compliance with crop rotation.
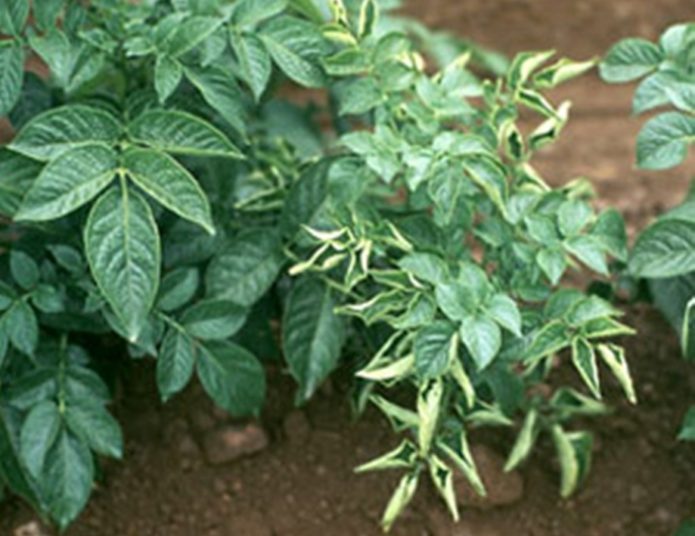
Leaf roll virus
Viral manifestations are caused by the PLRV pathogen - Potato Leaf Roll Virus.
Causes:
- infected mother tubers;
- transmission of the virus by aphids or field bugs;
- contact of healthy plants with sick ones;
- the presence of mechanical damage.
How to get rid and avoid:
- complete removal of a diseased plant;
- regular check of seedlings;
- getting rid of bedbugs and aphids;
- weeding;
- antiviral treatment of tubers.
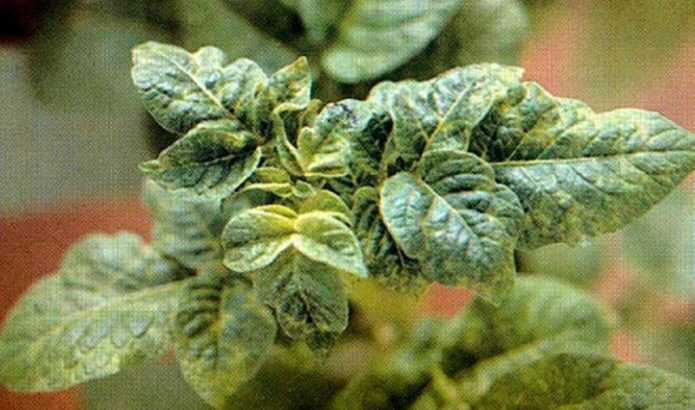
Potato wrinkled mosaic
The source of infection is the PVY virus.
Reasons for infection:
- mechanical contact with a diseased plant;
- infected potatoes;
- transfer by aphids.
Treatment methods:
- destruction of aphids;
- removal of diseased bushes;
- disinfection of seed tubers with insecticides and fungicides.
Background information on common potato diseases with photographs of manifestations will assist in recognizing the species, causes of occurrence and how to deal with the disease.