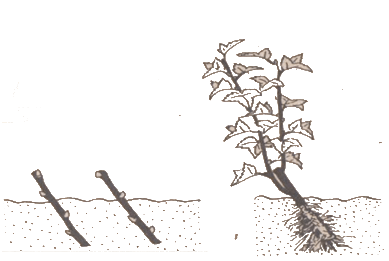Currant is one of the first shrubs planted by a summer resident on a newly acquired plot. Caring for it is quite simple, the harvest appears after a couple of years and grows quickly, the berries are tasty and very healthy. Reproduction of currants is also not a big deal. Let's consider how it is easier and more reliable to do this.
Content
The main ways of breeding currants
Currants, like any berry crop, can be propagated by seeds, but there is no point in this, since vegetative methods work out just fine and much easier. For black currant, the main methods of obtaining seedlings are propagation by layering and lignified cuttings, additional - green cuttings and dividing the bush. For red currant and its varieties (white, pink, etc.), the situation is similar, but its lignified cuttings take root somewhat worse than that of black currant.
Finished blackcurrant seedlings should have 2-3 main roots at least 25 cm long, and the aerial part should consist of 1-2 strong shoots at least 40 cm high.
Reproduction of currants by layering
As with all breeding methods, only healthy, productive bushes are suitable for growing cuttings. Usually, up to 5 good seedlings can be obtained from each healthy large branch per season.
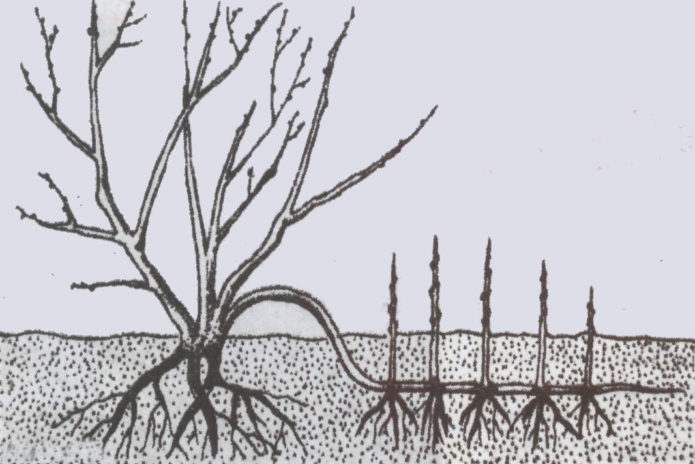
Rooted shoots on layers bent to the ground, as a rule, are formed on annual wood. The more growth the mother bush will have, the more rooted shoots will turn out from it. To enhance the growth of shoots, abundant pre-planting soil filling with fertilizers, especially manure and superphosphate, watering and rejuvenating pruning is necessary. As a rule, the shoots are bent in the spring before flowering (until mid-May), in low-winter varieties - in the fall. How to do it correctly?
We bend down annual basal shoots from each row in one or both rows. Before bending the shoots along the rows, we make grooves about 10 cm deep, 70–80 cm wide, into which we put the shoots at a distance of 8–10 cm from one another. We press the shoots to the ground by any means at hand, most conveniently - with staples made of thick wire. Cut the tops of the laid shoots to 5-6 cm.
Do not sprinkle the branches laid on the layers immediately. The first powder is applied 5–7 cm, when the shoots that have grown on the layers reach 10–15 cm. After about 2 weeks we add 5–7 cm a second time. Each powder is timed to water or rain. On the layers, root formation is most intense in June, after the first dusting, and in late August - early September. Watering during these periods effectively affects the development of roots. After watering, it would be nice to slightly loosen it up, but the best way out in this matter is usually mulching with any loose material.
We start digging the layers at the end of September.Usually by this time they already have powerful roots, allowing you to cut off the layers from the mother bush. We wash the leaves by hand. Layers that are not ready for planting as seedlings are planted for growing in a separate bed, and well-formed seedlings are planted in a permanent place.
If you do not add a whole branch, but only its upper part, you can get the so-called arcuate layering.
Propagation of currants by lignified cuttings
This is the most common breeding method, especially where there is a lot of rainfall. However, in arid conditions, the yield of seedlings with this method is only 30–40%.
Currant cuttings, and other shrubs, are propagated to preserve their favorite variety. But the advantages of this breeding method include the fact that currants will begin to bear fruit as early as next year:https://flowers.desigusxpro.com/en/yagody/smorodina/razmnozhenie-smorodinyi-cherenkami-vesnoy.html
The optimal timing for harvesting and planting cuttings of red currants in most regions of the country is the first days of September, in some places even the end of August. For black, the dates are slightly shifted forward, up to the beginning of October. The soil temperature at this time is quite sufficient to create favorable conditions for root formation during irrigation. Currant buds, which have entered a dormant state, no longer germinate at this time. In the spring, both roots and buds continue to grow simultaneously.
So, ripe cuttings are cut from annual growths 18–20 cm long and 8–10 mm in diameter. We take cuttings from fruitful healthy bushes with ripe buds. We immediately break off the leaves.
In the fall, we plant the cuttings on fertilized and well-dug beds, placing them 15–20 cm apart from each other obliquely along the row (almost 45about). We leave only 1-2 kidneys outside. Water and mulch immediately. If the weather is warm, sunny, you can shade them for the first time with newspapers or any other convenient material. This is how well-ripened cuttings look suitable for rooting.
For the spring planting of black currants, cuttings cut in the fall are first stored dug in, pouring water. Cuttings of red currant during spring planting take root very poorly, it is propagated only in autumn. To protect from freezing, the cuttings are covered with foil. When the snow falls, the bunches of cuttings must be removed from the pit and laid in the snow, burying deep and covering with straw.
In the spring, we plant cuttings in the garden bed when the soil warms up a little, but this should be done as early as possible, preferably “in the mud”. In the spring, they practice an almost vertical landing. We leave two kidneys outward, and one of them should be located near the ground. After correct autumn planting of currants we mulch the garden bed or simply spud the cuttings with soil. Care is usual - weeding, watering, loosening. In dry conditions, water more often. Against pests and diseases, it is necessary to carry out the whole range of health-improving measures.
In the first year, 2-3 shoots will grow from cuttings. We leave them in this form until spring, and then we cut them off almost completely (leaving a maximum of 10-15 cm) to stimulate the emergence and growth of new shoots. We leave the plant for another season and only in the fall, already in the form of excellent seedlings, will we transplant it to a permanent place.
Reproduction of currants by green cuttings
With this method of reproduction, film shelters and artificial fogging are used. Fog, settling on the leaves, forms a thin film of moisture, which protects them from drying out and overheating. If it is not possible to create artificial fog, you can try using a regular greenhouse, but the probability of success will be lower. The term of cuttings is the beginning of the decay of the growth of shoots (that is, the beginning of their lignification). In the middle zone, this is mid-June.
For harvesting green cuttings, the upper part of the shoots that appeared on last year's growths is most suitable. From the tops we cut pieces up to 20 cm long, and then we cut them into cuttings with one internode (we get pieces 5-6 cm long). Leaves, except for the top pair, are cut off. For better rooting, they can be kept for 6–8 hours in a solution of heteroauxin (half a tablet per 1 liter of water).
The substrate for grafting is river sand, poured into a layer of 3 cm on fertile soil, or a mixture of peat and sand (1: 1). We plant the cuttings at a distance of 5–8 cm to a depth of 1–1.5 cm and keep them under a foil until rooting.
We leave the rooted cuttings in a greenhouse until spring, and then we plant them in open beds.
A step-by-step description of transplanting currants to a new place:https://flowers.desigusxpro.com/en/yagody/smorodina/peresadka-smorodinyi-vesnoy-na-novoe-mesto.html
Reproduction of currants by dividing the bush
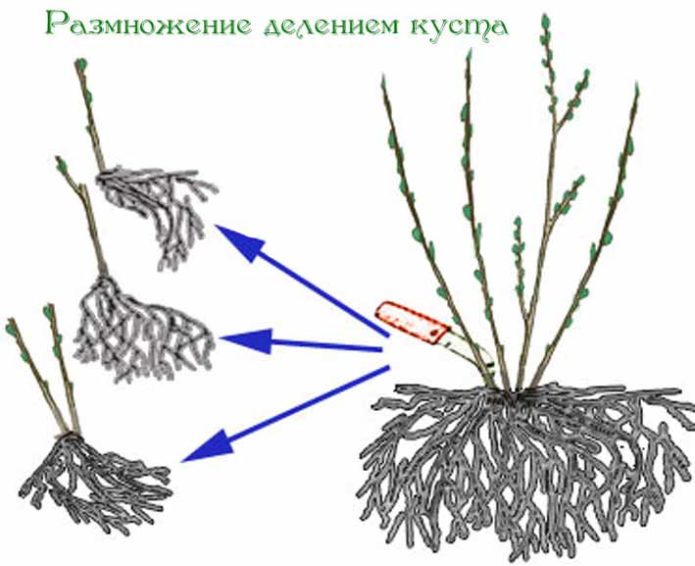
Dividing the bush into parts is not the main way of propagating currants, it is rarely used, mainly not for the purpose of obtaining new seedlings, but simply along the way: sometimes you have to transplant the bush to another place. Well, you didn't like where he was planted a few years ago, you want to build a place for barbecue here! Another reason may be a lack of normal planting material: they missed the deadlines for harvesting cuttings or did not make layering on time. Or maybe the cuttings were done incorrectly and no new seedlings were formed. Then you can dig up an adult bush and divide it into several parts. After all, they do this not only with currants, but also with most shrubs and perennial flowers. With peonies, for example, irises, etc.
The technique of dividing a bush is completely simple. The bushes are carefully dug with a shovel and divided into parts, each of which should have two or three branches with good roots. If suddenly the division of the bush was conceived in advance, then a year before digging most of the branches can be severely cut. Then the bushes will have time to form more young shoots. But more often than not, the thought of a transplant comes suddenly, so we act as follows.
Let's take a closer look at the bush as it grows in place. After all, it clearly has unnecessary branches: weak, dry, broken, crooked, etc. First, they are useless in new seedlings. Secondly, they will simply interfere with the digging. Therefore, we immediately cut them out as close to the ground as possible. The best young branches (1–2 years old) are slightly pruned (we cut off the tops of 10 centimeters), and for the rest, not the youngest, but still good ones, on the contrary, we leave 20 centimeters from the ground. Of course, this pruning can be done after digging up the bush, but the more compact it is, the easier it is to dig!
Having dug a bush, lightly shake off the ground in order to better see the roots and choose the right places where we will cut. Pruner, ax, saw, sharp shovel - whatever is more convenient for you. So, we divide the bush into parts so that they have several strong branches with their own roots. These should be both rather thick roots and lobes of young roots. There should be well-developed buds on the branches or at the base of the roots, from which new shoots will soon grow. We immediately remove unnecessary parts of the roots: old, sick, broken ones.
If possible, we immediately plant new bushes in a new place. When planting, we deepen them a little compared to the previous position. Pour a layer of earth above the upper roots at least 5 cm.
Propagation of currants by grafting
Why do you need a vaccination when breeding currants? After all, varietal qualities are perfectly transferred with the methods discussed above, and they are performed without much hassle. One could say that vaccination is done only out of curiosity. But this is not entirely true, or not always the case. Grafting currants allows you to perform other tasks as well.
For example, grafting speeds up the multiplication of a scarce variety in the absence of a sufficient number of cuttings.Or it helps to strengthen the red currant bush by grafting it onto the black root system. But most often the vaccination is performed if you want to get currants in standard form. Grafting is a reliable way to get a fruitful currant tree for those who want to turn their site into an unusual garden.
What rootstocks are currants grafted onto? In principle, you can graft anything and anything, and often "it" will grow. Indeed, cases of grafting currants on cherries have been described. This resulted in a currant tree with large berries. True, their taste is described as "strange". Still, the story that Michurin crashed when he climbed up the tree for apples, but he was crushed by a watermelon, carries something in himself. In nature, the like is always combined only with the like, and only gooseberries can be recommended for grafting currants from other crops, and let's leave the exotic to the experimenters.
The ideal option is seedlings of golden or fragrant currants, especially if they want to get a plant in a standard form. They are grafted onto annual shoots at a height of about 1 meter. Vaccination is done with the usual well-established techniques in horticulture. Black currant bushes of any variety that is sustainable in local conditions can also be used as a stock.
If you still want a golden one, but there is no bush, you will have to pre-grow it, having obtained at least a stalk of golden currant somewhere and grow a stock from it. Of course, it will take time, but in the case of currants, vaccination is more fun than a harsh necessity.
Usually currants are grafted in early spring. Much depends on the weather and the region, but the approximate date is usually the end of March. Ideally - the beginning of sap flow on the rootstock, until the buds began to bloom, but only swelled.
How to choose and plant currant seedlings correctly:https://flowers.desigusxpro.com/en/yagody/smorodina/posadka-smorodinyi-vesnoy-sazhentsami.html
Inoculation can be carried out throughout the summer, but the budding technique is somewhat more complicated, and the results from the amateur gardener are less predictable.
For spring grafting, cuttings are harvested in the fall, after the branches have stopped growing, the buds are well formed, that is, around October or even later. The best cuttings thickness is about 5 mm. The cuttings should have 3-4 buds, the cuts on both sides are covered with garden varnish and stored at a low positive temperature and a relative humidity of about 70%.
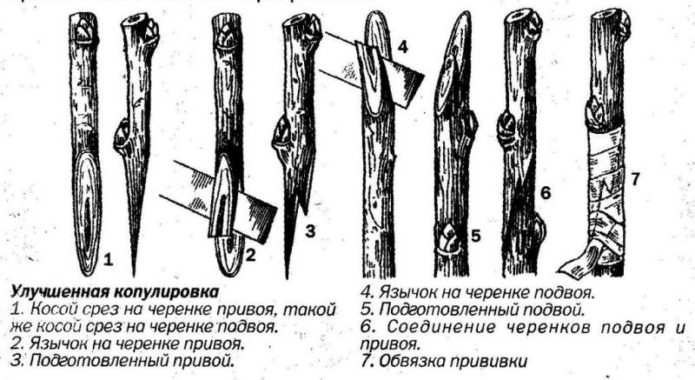
You can graft currants using any proven method: budding, copulation, splitting, lateral incision, etc. If we are going to get a currant tree, we choose the method of improved copulation and proceed as follows.
We leave only one strongest vertical shoot on the rootstock and look for a cutting that is ideally suited to it in thickness. At the bottom of the cutting we make an oblique cut, the length of which is three times the thickness of the cutting. To guarantee survival, soak in a growth stimulator for at least 15–20 minutes. We make a similar cut on the rootstock.
On the lower cut of the cutting, we make a small incision ("tongue") approximately in the middle of the oblique cut. Applying the cutting to the rootstock, carefully make a similar cut on the rootstock in the appropriate place and connect the cutting to the rootstock “tongue to tongue”.
We tie the vaccination site. It's good if you have a special grafting tape. If not - with PVC tape, glue layer outward. We cover the entire vaccination zone together with the strapping well with garden pitch. We also cover the upper cut of the cutting.
We destroy all the buds below the grafting on the rootstock and tie the future currant tree to the stake. We will remove the harness not earlier than in a year.
Well, and a very simple and free way to obtain planting material is shown in the next small video.
Video: new bushes from the old
Features of the reproduction of varieties of currants
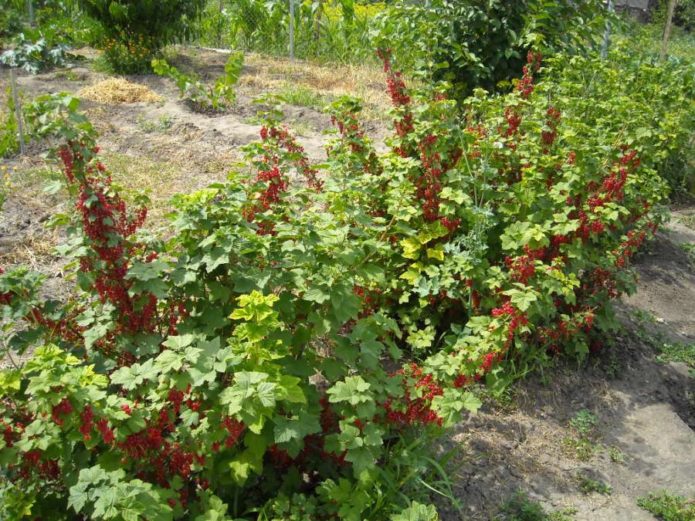
The name "red currant" is a common name, it is a whole group of varieties that have different colors. It can be red, white, pink, etc. The nature and properties of all these varieties differ significantly from the nature and properties of black currant.
The red currant bush grows more slowly. But an adult bush, as a rule, is taller than that of a black currant and can reach 2–2.5 m. Fruit formations are located on 2–5-year-old wood. The first berries appear in the third year. The main branches keep fruiting for up to 8 years, the whole bush can yield more than 20 years. Red currants are propagated by layering and cuttings.
How to speed up the reproduction of red currants
Red currant varieties love somewhat different living conditions than black currants. Cultivation of red currants works best in sunny areas, gentle slopes, with a fence from the winds. It needs less water than black currant, which responds extremely negatively to the slightest drying of the soil. The soil for red currants should be loamy or sandy loam.
If the soil on your site is acidic, for the successful reproduction of red currants, it is imperative to alkalize it by adding chalk or limestone. The best red currant seedlings are bushes from two years old with 3 skeletal roots. The optimal breeding method is horizontal layering. Reproduction by lignified cuttings is also good. True, some varieties of red currant cuttings reproduce with difficulty.
When propagating by cuttings, you can root them at home in convenient containers (pots, plastic bottles, etc.) to speed up the process. They do this even in winter, in conditions reminiscent of summer. Cuttings cut in the fall take root well over the winter and give young shoots. Thus, in the spring, a ready-made seedling can be planted in open ground, moreover, together with a lump of earth from the pot.
To accelerate the production of red currant seedlings, propagation by the so-called "combined cuttings" is often used. They do this right in the garden during the summer, but frequent watering is a prerequisite. They start work at the end of May. A combined stalk is a piece of bush in which, below the base of green shoots, about 6 cm high, there is also a two-year-old wood several centimeters long. Thus, in the mother bush, it is necessary to choose two-year-old healthy large branches that have managed to give many young shoots. It is from them that the cuttings are cut. All the leaves on them are preserved and cuttings are planted to a depth of about 4 cm, at a convenient distance from each other. Watering should be very frequent before roots appear! But by the fall, excellent seedlings are obtained.
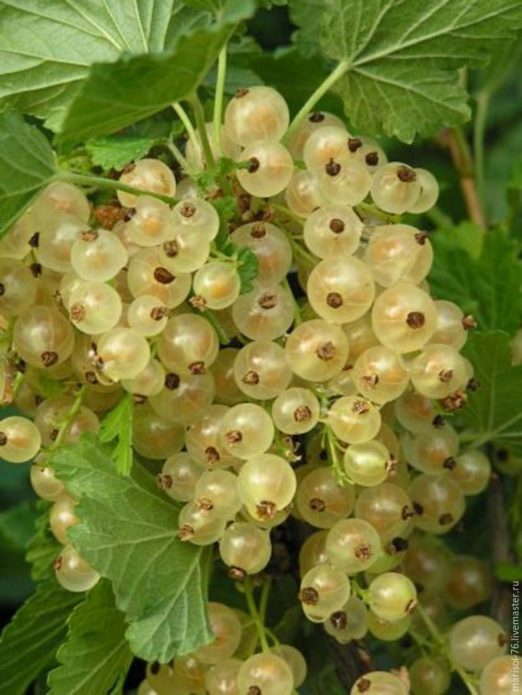
Reception of rapid reproduction of white currant
Varieties of white currants, since they are a variety of red, are quite frost-hardy. White currant berries can be transparent and also have any shade from cream to golden yellow. White currant grows well in the wild in central Russia and Belarus, often along river banks, local residents often even call it "Parechka". However, cultivated varieties of white currant, like red in general, are planted in summer cottages in sunny and non-swampy places. The optimal way of propagation is by horizontal or arched layering, somewhat worse - by cuttings.
As with red currants, white seedlings can be grown at home in winter to save time. In detail, the technology looks like this.
At the beginning of winter, cuttings are cut from one-year-old strong shoots of a healthy bush, and the entire branch is cut, practically from the ground. Cut it into cuttings 18–20 cm long and put in a jar of water, just like a bunch of flowers. As well as for flowers, a little honey or sugar is sometimes added to the water. The jar with the "bouquet" is kept in a warm place. For a long time, until the roots appear. It could be a whole month.During this time, the pots are prepared.
The pots can be made of any material, but it is imperative to put drainage from coarse river sand or small pebbles on their bottom. The substrate is ordinary soil with the addition of sand and a small amount of complex mineral fertilizers (it is possible without them if the land is fertile). Cuttings are planted one at a time in pots when their roots grow well. The ideal length is about 5 cm: longer ones will already be difficult to straighten, but easy to break off. How to deepen? It is best if two buds stick out.
The land must be well watered and the pots must be placed in a warm place, periodically watered and waited. Pretty soon, buds should swell on the cuttings, and by May, good seedlings should grow. With leaves. In mid-May, with a lump of earth, you can land them in a permanent place. If flowers decide to appear on the seedling, it is better to cut them off, the bush is not yet ready to spend energy on fruiting.
How golden currants reproduce
Golden currant - a native of North America, where it, like a similar variety - fragrant currant - is found in abundance in the wild. In our country, it is rarely found in the wild, but in a number of areas of the Volga region it has long been specially planted along highways as a pretty fence and an absorber of bad substances. So, no matter how much you want, collecting it along the roads is still not worth it. It is extremely unpretentious, for which recently our summer residents have been trying to plant it on their plots. It is often planted as a hedge, which requires a lot of seedlings.
Golden currant reproduces in all ways, like other types of currants: cuttings, layering, root suckers, dividing the bush, seeds.
There is only one nuance in its reproduction. Cuttings from annual growths are better harvested longer than for the familiar varieties of shrubs, since it takes root the worst of all. Cuttings are planted at the same time as red currant cuttings: at the end of summer, after soaking them in water for 2-3 days. Planting is constantly and intensively watered and mulched
Currants are a representative of that group of garden plants, with the reproduction of which there are no special problems even for novice summer residents. Getting planting material in the right quantities is quick and easy; there are only a few reliable ways to do this. And in a few years there will be only one problem: what to do with the rich harvest.